In today’s day and age, we come across thousands of software’s every day, and with the advancement in technology, software’s have made life easier.
Be it a windows device, or a mobile phone running Android, the advancement in software development has provided easy access to better software. That said, every piece of software is not created equally, and some software’s are created to hamper the way a computing system performs. Such malicious software is known as malware, and there is more than 1.1 billion malicious software out there.
Malware is a software designed to access, manipulate, or delete the data on a computer system to the benefit of a third party without getting the end-users consent.
Although people are under the impression that black hat hackers are the ones who create malicious code, organizations like. In the past, Sony has also used malware to prevent people from replicating music CDs’. There are several types of malware’s, and in this article, we will be talking about the various types of malicious software in detail.
Also read: What is the difference between Router and Switch?
Virus
A virus is a type of malicious software which is very similar to a biological virus. Just like a biological virus, a computer virus is harmless without a host program.

A computer virus is a piece of code which infects an executable file on the computer system. Once this infected file is executed, the malicious code is executed, and the virus can spread to other executable files. After replicating several times, the virus executes the payload it carries, harming the infected system.
To better understand how a virus works, let’s take an example of clicking on a link infected with a virus.
Once you click on the infected link, the malicious code runs and infects your system. The virus can enter your processor’s memory or the boot section of your computer on the infection. If it infects the boot section, the virus will run and replicate every time your system boots up.
After replicating several times, the virus releases its payload which can corrupt hard drives, display messages or slow down your system.
Worm
Contrary to a Virus, a worm is a self-sufficient malware that replicates itself on a computer network to reduce performance or eat up a network’s bandwidth.
Worms do not depend on other software installed on your system to function. Instead, they target vulnerabilities in the operating system to replicate and create havoc. Although worms were created to self-replicate and not cause any harm the systems they affect, newer versions of this malicious software have payloads capable of encrypting, modifying, or deleting user data.

Older versions of worms used infected floppy drives or CDs for infecting systems; newer versions rely on infected emails, instant messaging apps or infected peer to peer file transfer networks to attack users.
In case of an email worm, the malicious software enters the system through an email with the malicious code embedded in it. As soon as the user opens the attachment on the malicious mail, the worm installs itself on the system and tries to look for security vulnerabilities on the operating system.
Once it has gained access to the system, it creates copies of itself and sends infected mails to all users on the targets mailing list. The worm keeps repeating this process until the security vulnerabilities are fixed, making it a dangerous malware form.
The Wannacry cyberattack was also carried out using a worm which exploited the SMBv1 protocol in windows systems to attack systems.
Also read: Ransomware vs Malware vs Spyware
Spyware
Spyware is a piece of malicious software which is designed to collect personal data of the target. This information might include login credentials, banking information or other kinds of confidential information the user might enter on their system. This information could help the attacker in penetrating other organisations or to siphon money from their bank account.
There are various types of spyware, and keyloggers are a category of software used to keep a tab on the keys a target presses. Using this information, attackers can access personal information that can be sold on the internet or carry out other attacks.
Adware is also a type of Spyware which collects user data and sends to ad servers for user profiling and revenue generation.
Adware
In today’s day and age, most of the free services we enjoy are monetised by advertisements, and we are used to seeing pop-up ads on the apps we use every day. That said, some malicious software’s are designed to bombard users with unwanted advertisements.

Although Adware is generally not malicious, it collects user browsing habits and location data to profile users to show targeted ads. Adware is mostly bundled with free software available on the internet to generate revenue from people using free software.
Adware works by connecting target computers to ad servers which send pop up ads to the system making the user experience less rewarding. In some cases, adware changes the default search engine on systems to direct targets to websites that pay the attacker to redirect traffic to their website.
Adware could also redirect targets to websites with other malicious software that could harm the users’ system.
Also read: What is Bloatware and why is it detrimental to the users?
Rootkit
Rootkit tops the list when it comes to malware which is really hard to detect. A rootkit is malicious software that hides in a system by manipulating the operating system or infecting the bootloader or the BIOS. Due to this reason, it is tough to detect and remove rootkits.
Apart from all this, rootkits enable hackers to access the systems’ administrative access, allowing them to collect all kinds of information and manipulate data on the attacked system.
Due to the kind of access a rootkit provides to an attacker, they can be used to remotely access the attacked system and perform and attack the attacker wants to carry out.
Logic bomb
A logic bomb is a malicious software which executes when a set condition is true. Once the condition is satisfied, the malicious software will deploy its payload, which can be used to cause harm to a system.

Due to the way logic bombs are designed, they remain dormant on systems for long periods of time, making them hard to detect.
When it comes to using logic bombs, a contractor working for Siemens used logic bombs to corrupt spreadsheets to earn by getting paid for fixing the crashed systems.
Also read: What is code-signed Malware and ways to protect your device
Botnet
Botnet malware infects several computing devices and uses them to carry out DDOS attacks, spread malware, or carry out phishing attacks.
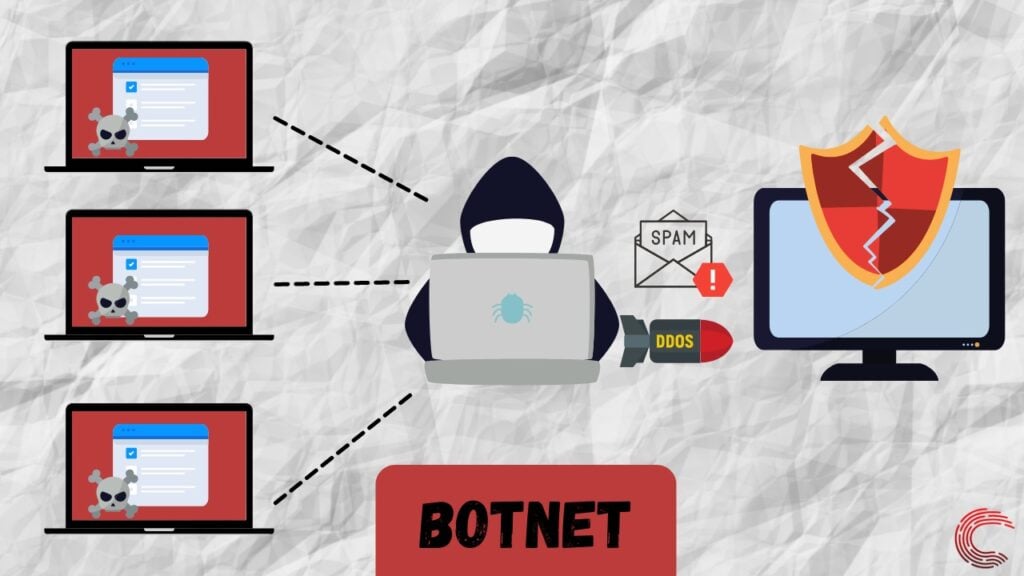
In a botnet attack, an attacker infects several computing devices with malware and uses them to attack other systems. If a system is a part of a botnet, the user might not realise that their system is being used to carry out a cyberattack as the user has no information about the infection.
Systems which are attacked by this malicious software could generate high internet bills, show slow performance and even lead to legal implications if the system is compromised during an attack.
Ransomware
Ransomware encrypts user data and prevents users from accessing it until and unless a ransom is paid.

Ransomware can be spread using different attack vectors, but it mostly uses system vulnerabilities and email phishing attacks to infect systems.
The Wannacry Ransomware attack infected millions of computers worldwide, taking payments in cryptocurrency.
Also read: 9 ways to secure your PC against a ransomware attack
Fileless malware
Most malicious software’s reside in filesystems, and most antivirus software’s analyse signatures of files to detect malicious software.
Fileless malware is a type of malicious software that does not create files; instead, it runs in the attacked system’s memory by running scripts on the system. Fileless malware uses Powershell, Word, or any other legitimate software to run malicious scripts that download executable files and runs them in the system’s memory.
Due to the design and attack vectors used by fileless malware, it is hard to detect, and keeping your system up to date is one way you can protect yourself from such attacks.
How to protect your system for malware?
As you can see, different malicious software’s use different attack vectors and payloads to infect systems. Therefore, one must take several precautions to protect systems from getting infected.

As developers keep patching security issues, keeping your system up to date is a quintessential task ever user must perform to protect their systems from malware. Making regular backups of your system at numerous places is also a good idea as it can help you recover data if Ransomware infects you.
Apart from this using a good antivirus in tandem with the windows defender is a good idea as it can help protect your system from additional threats. Keeping tabs on your internet bills is also a good idea as it can help you detect a botnet infection. Using virtual keyboards while entering sensitive information can prevent spyware from gathering sensitive information through keyloggers.
You can also keep checking your storage to detect worms in your system as they multiply exponentially, taking up a lot of storage. If you find any corrupted files or pop-up ads on your system, you should run an antivirus scan as your system might be infected by an adware or malicious software.
Also read: What is an NFC attack? How does it work and 3 preventive measures