Having a flagship as your daily driver is always a delight, and with every passing year, the computational power of these handheld beasts incrementally go up. From recognising faces to voice searches on the web, the modern smartphone can do things that were unimaginable a decade ago.
The semiconductor industry’s growth is the biggest contributing factor to this change. When it comes to silicon that power your smartphones, Qualcomm is the name in the game spanning over 32% of the Android smartphone market.
Every year Qualcomm updates its Snapdragon processors and keeping up with the trend, it released the new Snapdragon 888 processor to power the flagships of 2021 — well at least those coming out in the first half of the year.
So, if you plan to buy a flagship and can’t decide between a device powered by Snapdragon 865+ and 888 you have come to the right place. In this article, we will be talking all about there is to the new Snapdragon 888 and how it compares against the older Snapdragon 865+
Also read: Snapdragon 865+ 5G vs 865 5G vs 855+ vs 855
Manufacturing process
An SoC’s manufacturing process is a critical factor in influencing the chip’s power consumption and processing power. A smaller manufacturing process enables chipsets to have lower power consumption and high computational power as more transistors can be etched into the same silicon.
The Snapdragon 865+ uses a 7-nanometre manufacturing process, whereas the new Snapdragon 888 uses a 5-nanometre process. Hence the 888 can offer better power to performance ratio when compared to the older 865+.
CPU
Although the Snapdragon SoC has multiple components, the CPU performs all the operating system’s computational tasks to function properly. Therefore, having a beefier CPU helps.
Being the flagship process of Qualcomm, the Snapdragon 888 has the most powerful CPU in Qualcomm catalogue. Both the Snapdragon 865+ and the 888 have an octa-core design with a tri-cluster architecture, but they use different ARM cores.
The 865+ is powered by a high-performance Cortex-A77 (Kryo 585 CPU) clocked at 3.1GHz, three Cortex-A77 gold cores at 2.42 GHz, and four Cortex-A55 silver power-efficient cores at 1.80 GHz.
On the other hand, the Snapdragon 888 uses Cortex-X1 super core (Kryo 680 Prime CPU) at 2.84 GHz, four Cortex-A55 silver cores (Kryo 680 Efficiency CPUs) at 1.80 GHz, and three Cortex A78 gold cores (Kryo 680 Performance CPUs) clocked at 2.42 GHz.
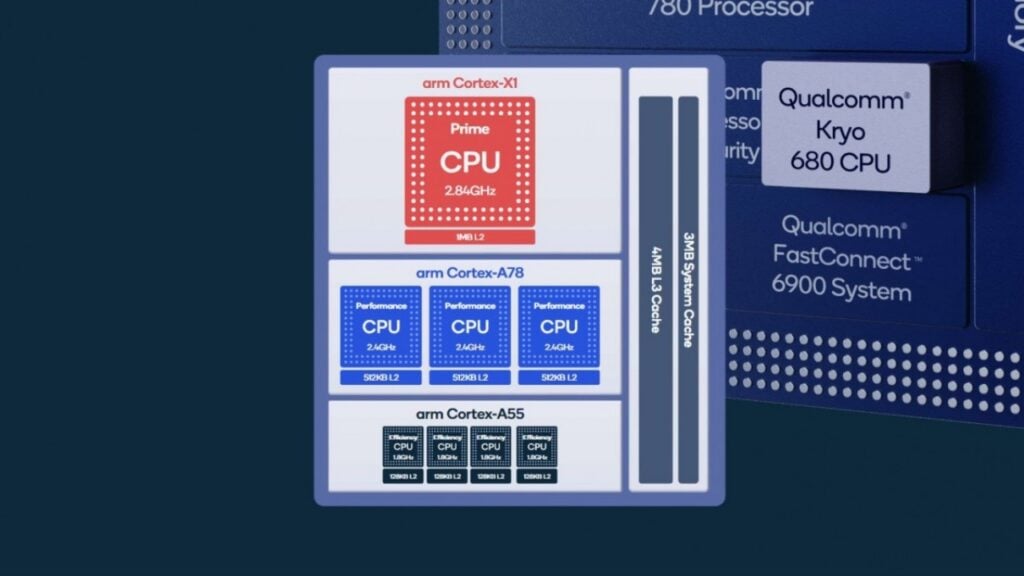
Although both the CPUs use different clock frequencies, the Snapdragon 888 uses newer cores which offer better performance and higher power efficiency. In terms of numbers, ARM claims that the Cortex A78 offers 20% higher performance when compared to the A77 on a 1-watt budget.
Simultaneously, they take 15% lesser space on the silicon when in a quad-core configuration as each core is 5% smaller compared to previous generation processors. The newer cores also consume 50% lesser energy while delivering similar performance than the older A77 cores.
The new Cortex X1 core on the Snapdragon 888 is the first processor developed in the CXC program. It offers 23% faster integer calculations than the A78 performance cores and 30% faster computation than A77 cores. Due to the higher computational power of the X1, it consumes more power compared to the A78 cores.
Qualcomm claims that the Kryo 680 package offers 15% more computational power when compared to Kryo 585 on the Snapdragon 865+.
Also read: Helio P70 vs Snapdragon 660: Which one is better?
Gaming and GPU performance
The Snapdragon 888 is powered by the Adreno 660 compared to the older Adreno 650 on the Snapdragon 865+. When it comes to specs of the GPU, Qualcomm does it reveal a lot. That said, the company claims 35% faster graphics rendering and a 20% increase in power efficiency.

Apart from all this, the Snapdragon 888 comes with Qualcomm’s game quick touch technology that reduces touch latency by 20%. In addition to this, devices using the 888 can leverage Snapdragon elite gaming platform that enables HDR games to run twice as faster.
It also supports 10-bit HDR rendering improving the contrast ratios of the game. This technology also brings desktop level technologies like variable-rate shading to mobile devices and enables users to update their GPU drivers, which means users don’t have to wait for a software update to optimise their gaming experience.
Also read: All Intel processor generations compared
Camera and image processing
The Snapdragon 888 is powered by the Qualcomm spectra 580 ISP, an updated version of the older spectra 480 ISP. This new ISP enables the Snapdragon 888 to capture and process 2.7 gigapixels in a second, which translates to 120 burst images at a resolution of 12 megapixels in a second
Compared to the older ISP this unit shows an improvement of about 35% and has three independent ISPs — one more than 865 plus. This setup enables the 888 to shoot 4k video from three cameras in real-time and indulge in 10-bit HDR photography.

In addition to this, a new low-light architecture has been added to the chip, improving low light photography. Also, computational HDR can be used while recording 4k videos, and AI-assisted autofocus feature is also added with this new ISP.
Also read: Snapdragon 712 vs 710 vs 675
AI
The most significant improvement on the Snapdragon 888 can be seen in the AI processing area, which elevates the overall experience of gaming, photography and networking as AI algorithms are used intensively in these areas.
The Snapdragon 888 uses the all-new hexagon 780 AI processor with a fused design, which incorporates the scalar, tensor and vector units into a single core, improving the chip’s AI computational power. In addition to this, the AI core is connected to 16 times larger memory unit, enabling bigger AI algorithms to be accessed in a single time.
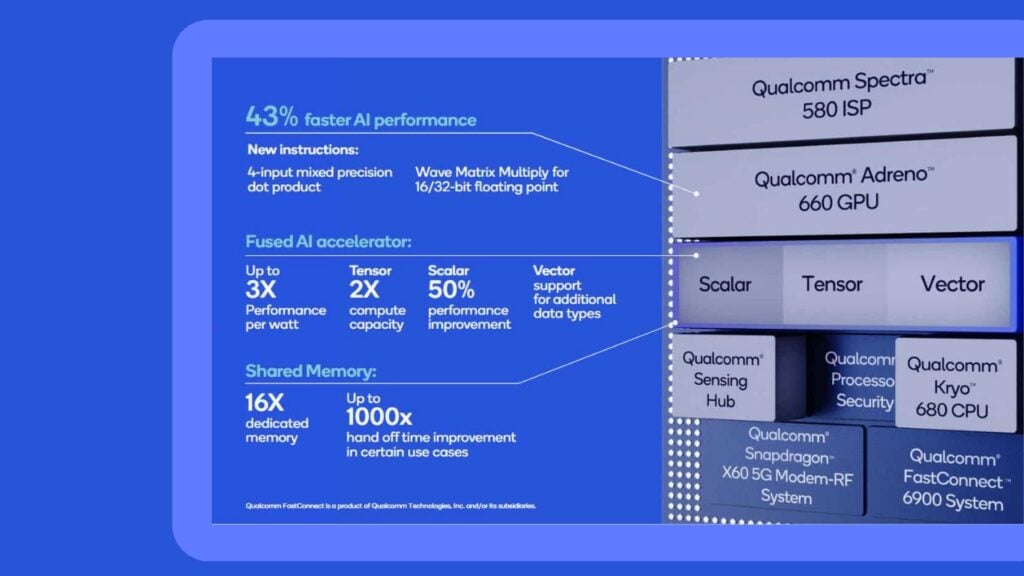
In terms of numbers, the new AI core enables the Snapdragon to carry out 26 trillion operations per second, which greatly improves the older chip capable of performing 15 trillion operations per second. The new chip can also perform tensor calculations at double the speed and scaler calculations are also improved by 50%.
Although the chip’s AI computational power is very high, it delivers this performance by decreasing power consumption three times than older generation processors.

In addition to the new hexagon 780 AI core, the Snapdragon 888 uses the second generation sensing hub, which is a power-efficient AI core responsible for running AI algorithms that run in the background to enable features like a smart wake up on trigger words like “OK Google” and screen wake up on movement detection.
The second-generation sensing hub offers 5 times faster computational power at less than 1 milliamps of power consumption. Due to the sensing hub’s power efficiency, AI algorithms can be offloaded from the hexagon core to the sensing hub to reduce power consumption.
Also read: Logitech G-Hub vs Logitech Gaming Software (LGS)
Security, networking and other improvements
In terms of networking the Snapdragon 888 uses the Snapdragon X60 5G modem, an updated version of the X55 modem, which offers better connectivity with various service providers. It is on power with the X55 and offers technologies like WiFi 6E with speeds of up to 3.6 gigabits per second.
When it comes to security, the 888 is the first mobile processor to offer hypervisor support, which enables users to run independent instances of different operating systems on their device. This allows users to have two different profiles on their device, and if one is compromised, the other profile will remain unharmed.

It also comes with Truepic technology, enabling the processor to fingerprint the pictures you take with cryptographic keys, which helps users make claims on their image’s authenticity in copyright infringement.
The chip also comes with the latest version of quick charge technology that Qualcomm claims can deliver a 50% charge in five minutes by supplying more than 100W power. This protocol also offers 70% more efficient charging while keeping devices 10 degrees cooler while charging.

This protocol also offers eight levels of voltage protection, three levels of current protection, three levels of thermal protection and USB input overvoltage protection at 25V and extreme power controls beyond 30V.
Also read: How to check and recover clipboard history on Android?
Benchmarks
Unlike every year, Qualcomm released the benchmarks of a demo device running popular benchmarking tools. The comparison for the various benchmarks is given below.
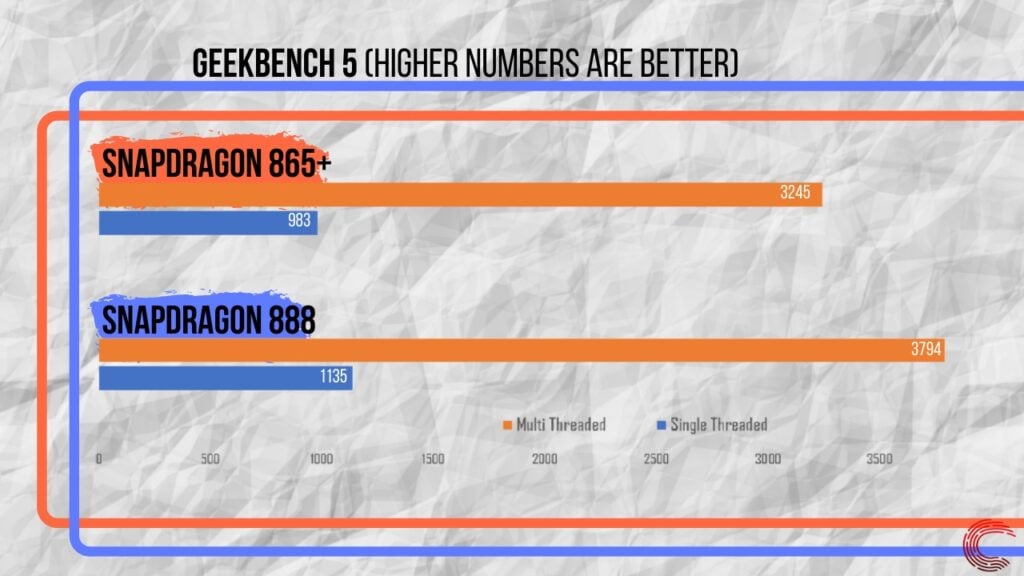
The Snapdragon 888 shows a 14.47% increase in multi-core performance. In the case of single-core performance, the Snapdragon 888 provides a 13.2% boost in performance.

The Gfxbench benchmark shows a 30% improvement in GPU performance and is close to Qualcomm’s claims, which can offer a relatively better gaming experience.
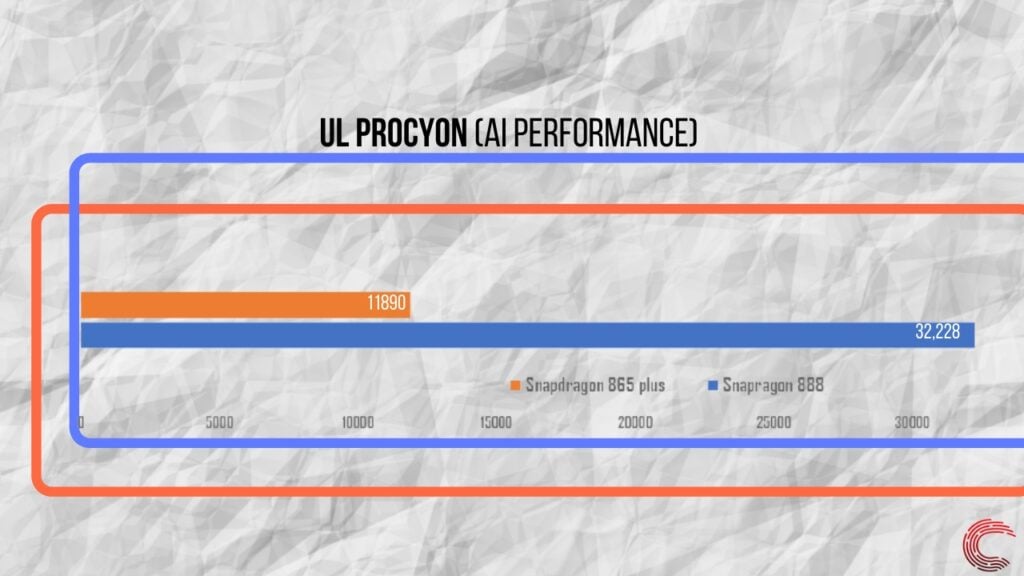
In terms of AI performance, the Snapdragon 888 offers a three times faster performance than the 865+.
Looking at the benchmarks, one can say that Qualcomm lives up to the claims it makes in terms of performance and will definitely provide significantly better computational power to the flagships of 2021.
Given below is a comparison of the specks each processor offers to help you make an informed decision on which SoC is better for you.
| Category | Snapdragon 888 | Snapdragon 865+ |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | Cortex-X1 super core at 2.84 GHz, four Cortex-A55 cores at 1.80 GHz, and three Cortex A78 cores clocked at 2.42 GHz. | Cortex-A77 clocked at 3.1GHz, three Cortex-A77 cores at 2.42 GHz, and four Cortex-A55 silver power-efficient cores at 1.80 GHz. |
| GPU | Adreno 660 | Adreno 650 |
| Lithography | 5 nanometer | 7 nanometer |
| Camera | Qualcomm spectra 580 ISP(Triple ISP setup) | Qualcomm spectra 480 ISP(Dual ISP setup) |
| AI | Hexagon 780 fused AI core | Hexagon 698 Processor |
| Security | Qualcomm secure processing unit with hypervisor support and Truepic technology | Qualcomm secure processing unit |
| Charging | Quick charge 5 | Quick charge 4+ |
| Memory | LP-DDR5 memory up to 3200 MHz | LP-DDR5 memory up to 2750 MHz |
Also read: OnePlus Band vs Mi Band 5: Which one should you buy?






